Equinor will no longer export gas to occupied Western Sahara

The Norwegian state-controlled energy company Equinor ‘regrets’ exports of gas into Western Sahara and promises to never do it again.
Published 10 May 2020
Illustration photo above: Gas Cerbeus photographed last year. (Photo: Gerolf Drebes)
In April, a vessel with liquified gas arrived at El Aaiún harbour in occupied Western Sahara, shipped directly from the terminal of the Norwegian energy company Equinor (former ‘Statoil’) in Kårstø, Norway. The incident was covered today by the Norwegian daily Dagsavisen.
This is the first ever documented case of exports of Norwegian gas to the occupied territory through all times. On 20 April at 05:41 am, the vessel anchored up outside the entry to El Aaiún harbour. Later that same day, it sailed into the capital of Western Sahara to offload its 4900 tonnes of gas.
In a letter to the Norwegian Support Committee for Western Sahara on 24 April, Equinor's vice-president confirms the shipment. The company stated that it ‘regrets' that it had not picked up the Norwegian government's business advice.
“We […] are now amending our procedures to capture the Norwegian position”, Equinor's vice-president Tor Martin Anfinnsen wrote the Norwegian Support Committee on behalf of the company president Eldar Sætre.
Equinor is the world's 12th biggest energy company and 2/3 controlled by the Government of Norway. The Norwegian Ministry of Foreign Affairs urge businesses not to engage in the territory.
In April last year, Norway’s Minister of Foreign Affairs stated in the parliament in Oslo that her government agrees with the decisions of the Court of Justice of the EU: international law requires the prior consent of the Saharawi people on matters relating to business in Western Sahara. Equinor has now a position that is aligned with that of other companies fully or partially owned by the Norwegian government, such as Yara, Cermaq and Mesta.
The clarification from Equinor came as a reponse to a letter from the Norwegian Support Committee to the company president on 21 April. Several of the aspects that the Norwegian Support Committee asked about were not answered by Equinor, particularly relating to whom had given the company permission to send the cargo in to the occupied territory. A second letter was therefore sent to Equinor on 25 April. That letter has not yet been replied to.
Equinor explained that the vessel contained a cargo of butane to its client Gulf Petrochem - or GP Global, which the company has changed name to. Western Sahara Resource Watch wrote GP Global on 24 April, enquiring whether they had obtained the Saharawi people's consent to import the gas, and whether Equinor had asked them about the aspect of consent prior to the transaction. The cargo was transported aboard the Liberian-flagged gas tanker Gas Cerberus. On 25 April, WSRW in Greece and the Norwegian Support Committee wrote a letter to the vessel's operator, Stealth Corp. None of these letters have been responded to.
Equinor clarified further to Dagsavisen newspaper today that the cargo was sold to GP, and that "this cargo has then been resold from GP to another client for delivery in Laayoune, and we shipped the cargo there for GP".
Data from the Norwegian statistics bureau Statistics Norway reveals the value of gas exports from Norway to Morocco over the last decade: In 2019, the value of the butane exports was at 290 million kroners (26 million Euros at 2020 exchange rate), while the propane exports was 357 million kroners (32 million Euros). The exports have also continued into the first months of 2020. There was a small exports of gas condensate to Morocco in May 2019, at a value of 7 million kroners.
It is not yet known whether the gas exported from Norway to Morocco is being reexported to Western Sahara.
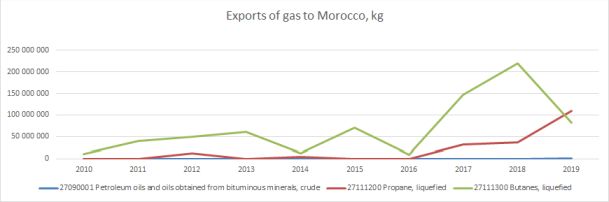
According to figures published by Western Sahara Resource Watch last week, 15 transports of gas took place in to the territory during the calendar year of 2019. All of it was either from Morocco or from the occupiers closest allies - Spain and France. 5 of the 15 transports came in to Western Sahara from Morocco - which is not itself a gas producing country. The Norwegian Support Committee asked Equinor on 21 April regarding what kind of due diligence Equinor carries out on its clients, and how it views that its clients could be reexporting gas from Morocco to Western Sahara. These questions were not responded to in the reply letter of 24 April.
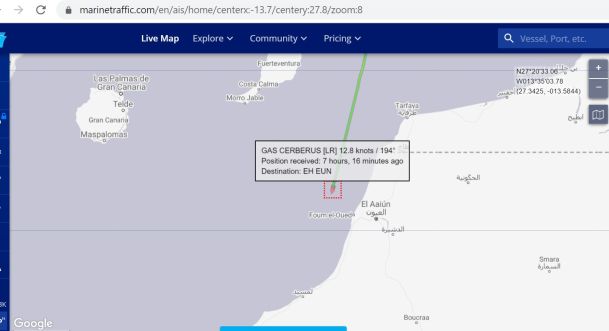
Gas Cerberus entered El Aaiún harbour on 20 April early afternoon.
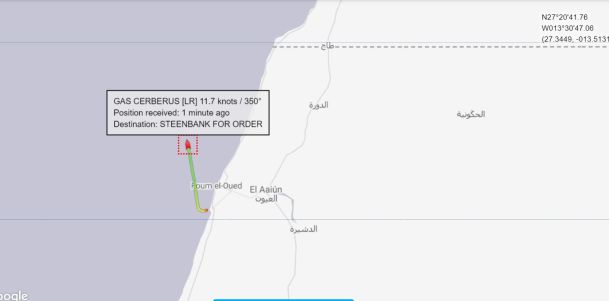
The vessel left El Aaiún harbour on 22 April, in the afternoon.
News
This port is the biggest exporter of gas into occupied Western Sahara
For the first time, Portugal is the biggest exporter of gas products into occupied Western Sahara.
15 May 2024
Norwegian gas transport avoids Western Sahara at last minute
A vessel transporting Norwegian gas was supposed to arrrive in occupied Western Sahara tomorrow, but has now steered away last minute, as ordered by the exporter in Norway.
06 June 2020
First overview of gas imports into occupied Western Sahara
50,000 tonnes of liquified gas arrived in occupied Western Sahara last year, according to our first overview of this key trade.
04 May 2020
Skretting Turkey misled about sustainability
Dutch-Norwegian fish feed giant admits using conflict fishmeal from occupied Western Sahara. Yesterday, it removed a fake sustainability claim from its website.
11 September 2025



